Breadcrumbs
Glossary of Audio Visual Terminology
-
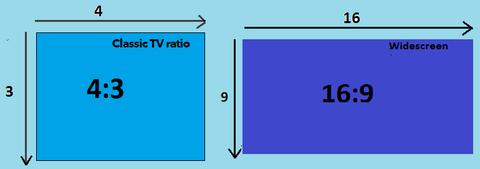
Aspect ratio
The ratio of the projection or display screen’s width x height. Most legacy systems and Microsoft Powerpoint presentations use the almost-square 4:3 ratio. The videoconference-equipped lecture room cameras, video conference systems and screens display in the 16:9 ratio. See here on how to change your 4:3 Powerpoint to 16:9.
Audience Response System (ARS)
Allows for students to respond simultaneously to questions posed in a live presentation, and for cumulative responses to be displayed on-screen. The MD Program currenlty uses Turning Technologies as the ARS. Questions are integrated into the Powerpoint presentation, and students use an app on their own devices to respond.
AVI
A video file type used in the recording process and is not usually distributed. Stands for Audio Video Interleave format, created by Microsoft Corporation.
BYOD
Stands for Bring Your Own Device, and refers to the requirement of some classrom technologies to operate on students' own devices, such as their laptops and smart phones. The audience response system used here is an example of the BYOD model.
In the videoconference-equipped lecture rooms in MSB and TDHSC, these are three monitors in a case, facing the lecturer, that replicate what is being shown to students on the large lecture room screens, in order that lecturers don’t have to turn around and look at the large screens behind them. The left monitor shows the lecturer camera and is a guide for lecturers to stay on camera and not walk off frame. The centre monitor shows content (such as Powerpoint), while the third shows a wide shot of the students at the remote site and close ups of students asking questions from either site.


Area that has access to most of the control technology for the videoconference-equipped lecture rooms, and from where control room staff can monitor lectures that are being videoconferenced. There is one control room in the TDHSC and one in the MSB, and both are in close proximity to the videoconference-equipped lecture rooms.
Professional videoconference technicians work behind the scenes in the control room and in the lecture rooms to set up lecture videoconferences, troubleshoot any issues, and maintain the equipment. Control room staff are present both at the MSB and TDHCS and are in close and frequent contact with each other via a separate HD videoconference unit located in the control rooms.
The information technology (IT) department for the Faculty of Medicine. The audio-visual (AV) unit of DC, with associated staff in Mississauga, is responsible for maintaining the technology for the videoconference-equipped lecture rooms, the operations of lecture videoconferencing, and other media-production related tasks and projects. Contact MedIT or 416 978-8504.
Document camera
A device that displays either 3D objects or pre-written text to the local screen or to videoconference audiences. One of these is in each of the four videoconference-equipped lecture rooms.
The MD Program's learning management system, implemented in August 2018
Entrada
The former name of Elentra
Far (Site, Audience, or Participant)
See Remote (Site, Audience, or Participant)
Field recording
A video and audio recording method involving the transport of video and audio equipment to locations outside of the studio. Discovery Commons’ field recording units can provide multi-camera, live webcast and computer display resources.
The measure of the size of a computer file, usually measured in bytes (B), megabytes (MB), kilobytes (KB), and gigabytes (GB). Video, audio, photography and graphics can take up a large amount of space on a hard drive. A one-hour MP4 video file can often be as large as 800 MB. Some video-file types, such as AVI, are better suited for recording but are too large for posting on the web. Other file types, such as MP4 and Adobe Flash, are more compressed and, therefore, better suited for web distribution and streaming. There is software that can convert large file sizes to smaller sizes for sharing or posting to the web.
Adobe Flash is a deprecated platform for showing video on the web. Flash has now been superceded by html5 as it takes precedence as a more universal format for web viewing.
Flipped classroom
Teaching method that requires students to watch a pre-recorded lecture before attending an interactive session with a teacher. This method contrasts to the traditional method in which students attend a lecture at school and then review the work at home.
Front projection
A projector’s beam projects to the screen from the audience side or front of the display. The videoconferenced-equipped classrooms in the Terrence Donnelly Health Sciences Centre in Mississauga use front projection.
Green curtain or green studio wall that allows for the removal of the colour green from the video spectrum, in order that the green background can be replaced with something else, such as a photo or video of another location.
High Definition quality video is any video with resolution higher than standard definition. HD is currently typically 720p,1080i, 1080p, or 4k. The numbers refer to the number of lines of resolution from the top to the bottom of the screen in a 16:9 aspect ratio, and the p and i after the numbers refer to the way the lines of resolution are scanned. The screen displays in the videoconference-equipped lecture rooms, as well as many of the recently installed meeting rooms, are 720p in a 16:9 aspect ratio.
Host (1)
A web host is a service that provides servers on which individuals and organizations can place material in order that it can be accessed from a website. Videos at Discovery Commons, for example, are hosted with the media hosting company Kaltura. A link to the video (url) is provided, and that link gets posted on a website, and when a user clicks the link, the video streams and can be viewed.
Host (2)
In a classroom videoconference, the host refers to the site from which the lecturer is presenting; in a fully remote videoconference, using a tool such as Zoom, the host refers to the account holder managing the call.
HSC
See Terrence Donnelly Health Sciences Centre
HTML5
Computer language for content on the internet, it includes features for playing audio and video within web pages with special considerations for playing media on smart phones.
Lectern Intercom

Located on the classroom lecterns, this intercom allows someone in the lecture room to communicate with a technician. It has a silver panel with a white microphone button. During a videoconferenced lecture, a presenter requiring technical help can push the button and be connected with a control room technician.
Lectern Microphones
The long-stemmed microphone on the lectern that is one of two default microphone options for presenters. The second option is a wireless lapel microphone usually found on top of the lectern or in a cubby in the lectern. If you stay behind the lectern, you can use the lectern microphone, but if you plan to move away, even a little, from the lectern while you are teaching, you must use the wireless lapel microphone in order that the remote site can hear you.
Sound adjustments are done by technicians, but there is a Privacy button on the touch panel on the lectern that will mute and unmute the lectern microphones. Pressing the Privacy button from flashing to solid changes both lectern microphones from mute to live; pressing it again so it is flashing sets them back to mute. Using the mute feature is advised for any time you are behind the lectern before and after your lecture, but are not teaching to the class.
In each of the videoconference-equipped lecture rooms, there are two cameras pointed towards the lectern: one frames the lecturer and the lectern only; the other shows a wider shot of the front of the room. The closer shot is the one used most of the time, and the other is used if the lecturer steps away from the lectern. The cameras allow the lecturer to be seen by students at the remote site, and they also facilitate a better view of the lecturer for those in the back of the room where the lecturer is presenting.
Lecturers are advised not walk up the aisles, as the cameras will not be able to follow them.
Lecture-Room Cameras
There are five cameras in each of the videoconference-equipped lecture rooms. Two cameras are pointed at the lectern; these are the lecturer cameras: one frames the lecturer and the lectern only; the other shows a wider shot of the front of the room. Three additional cameras are pointed at the students; these are the student cameras: one is a wide shot that shows all of the students, and the other two are used for framing students when they ask questions.
Lighting control
The lecturer can control the room lighting both in the lecture theatre and at the remote location in a videconference using the Lighting controls on the lectern panel. The three blue buttons will change lighting in the local and remote lecture theatres while the four grey buttons change lighting only in the local room.

Local (Site, Audience, or Participant)
Refers to the site, audience or participant in the videoconference location that is where the presenter is.
Two of the four videoconference-equipped lectures rooms are in this building located at University of Toronto St George campus; the other two are in the Terrence Donnelly Health Sciences Centre in Mississauga. Also known as the MSB.
Video file format that compresses and reduces the file size from the original version while delivering a good quality reproduction. Most of Discovery Commons’ edited video productions are output as MP4 files for viewing on a website.
Microphone Modes (Student Mics)
During videoconferenced lectures, there are four student microphone modes available in the MSB 3153, MSB 3154 and HSC130 and HSC140 lecture rooms. The default mode is Request to Speak, which will be appropriate for most lectures. Other modes may be useful for different teaching styles. Please discuss your requirements with a technician and the mode will be changed in the control room.
- Dynamic Mode – When the student presses the microphone button in front of them, that microphone becomes live. When the lecturer presses the Take Next button, the next microphone in the queue becomes live, etc.
- Request to Speak – When the student presses the microphone button in front of them the microphone does not become live until the lecturer presses the Take Next button. Each microphone in queue becomes live each time the Lecturer presses the Take Next button.
- Manually Operated – Student microphones can only become active when the lecturer presses the seat button representing the student’s seat in the local or remote room. Thumbnails for both rooms are located below the seat map.
- Student Directed – Students can select their own microphone or a group of microphones to be live. This mode is used for small group meetings. This mode works best when there are no more than six live microphones per room.
Post
A link to an item, such as a video, that is placed on a website. The item resides on a server somewhere, and when the user clicks the posted link, the video plays from that server.
A button on the touch panel in the lecture rooms that allows the lecturer’s microphones to be muted. When the Privacy button on the touch panel is flashing, both the lectern microphone and the wireless microphone connected to the lectern are muted. When the Privacy button is not flashing, both microphones are live.
Projector
A projector that sends laptop, lectern PC or other electronic display information to a screen.
Rear Projection
The projector’s beam projects onto the screen from behind. The videoconferenced-equipped classrooms in the Medical Sciences Building at the St. George campus use rear projection.
Remote (Site, Audience or Participant)
Refers to the site, audience or participant in the videoconference location that is not where the presenter is.
Room Volume
The overall volume level of the room. In the videoconference-equipped lecture rooms, the optimum level is 80%. Levels are adjusted by technicians in the control rooms.
Sharefile
File-sharing application for transferring large files available to Faculty of Medicine staff. This resource is excellent for those who want to share large video and audio files with faculty, staff, students both within and outside of the University of Toronto. Contact discovery.commons@utoronto.ca for account information. Sharefile is different from UTMedfiiles.ca, which is the tool that all presenters should use to send their presentations and any related materials to control room staff. Sharefile can be used to send files not associated with lecture -videoconferencing.
Single Camera Recording
The recording of a lecture or meeting with one video camera. If scripted and planned well, single camera recordings can be edited to look like a multiple camera recording.
SMART Monitor
The interactive monitor at the lectern of the videoconference-equipped lecture rooms that allows the presenter to use a stylus to annotate and advance slides. Annotations are displayed on the lecture room screens and are recorded along with the rest of the presentation (if recording has been initiated).
Sound Control
There are five sound control options available on the lectern’s touch panel in the videoconference-equipped lecture rooms. They are explained here, but are adjusted by control-room technicians.
- Sound /Lectern Microphone: The microphone can be enabled (on) or disabled (off). The microphone volume can be increased by pressing the + button or decreased by pressing the – button.
- Sound /Wireless Microphone: The microphone can be enabled (on) or disabled (off). The microphone volume can be increased by pressing the + button or decreased by pressing the – button.
- Sound /Video Volume: This controls the computer or any other device patched into the HDMI or RCA sound ports on the lectern. The video volume can be enabled (on) or disabled (off). The video volume can be increased by pressing the + button or decreased by pressing the – button.
- Sound/Video Conference Volume: This controls the volume from the lectern and student microphones at the remote location. The video conference volume can be enabled (on) or disabled (off).The video conference volume can be increased by pressing the + button or decreased by pressing the – button.
- Sound/Audio Conference Volume: This controls the volume from the lectern and student microphones at the remote location. The audio conference volume can be enabled/(on) or disabled (off). The audio conference volume can be increased by pressing the + button or decreased by pressing the – button.
Refers to the delivery and receipt of online video provided by a host service, allowing the user to view the video without downloading it.
There are three student cameras in each of the videoconference-equipped lecture rooms. One of the cameras is set to a wide shot of all of the students, and two cameras will automatically frame students when they ask questions.
When a student microphone button is pressed, the camera will frame the area where the student question came from. A second camera will frame the second person to press the microphone button and the cameras will alternate each time a student microphone button is pressed thereafter. When the student's microphone is live, the framed video of the student is available for the lecturer to see on the confidence monitor (this is the only way the lecturer will be able to see the student if the live mic is at the remote site). The students at the local site will also see the remote student on the large screen. When the student microphone is turned off, the screen will show either the wide shot of the students in the room or the next student camera, if there is another question or comment in the queue.
Student-Microphone Seat Map
Map of the lecture room student microphones in the videoconference-equipped lecture rooms, accessed via the touch panel. The lecturer can use the seat map to identify the location of where the question is coming from within the lecture theatre or to switch a microphone to live mode.


There is one microphone for approximately every two student seats in the videoconference-equipped lecture rooms. These microphones have a push-to-talk button, and the microphones are generally turned off until the lecturer turns them on, one at a time as necessary, from the lectern.
When a student presses their microphone button, a blue light around that button flashes. At the same time, the lecturer will get two separate indicators that a student wishes to speak: on the lectern in the form of a flashing blue light around the Take Next button, and atop the confidence monitor in the form of a solid red light. If the lecturer presses the flashing Take Next button on the lectern, the student's microphone will go live, their voice will be amplified in the room, and it will transmitted to the remote site. When the student is finished speaking, they will turn their own microphone off (by pushing their button again), or the lecturer can turn it off by pressing the Take Next button again.
Student Request-to-Speak Indicators
In the videoconference-equipped lecture rooms, a red light above the centre confidence monitor will turn on to indicate a student's request to speak in either the local or remote lecture rooms. At the same time, a blue light around the Take Next button lights up on the lectern.
Studio
Discovery Commons has a small video recording studio location available to the Faculty of Medicine to record educational projects and to broadcast live webcasts.High-definition cameras, professional lighting, green screen, microphones, and teleprompter are some of the available resources.


The button on the lecterns in the videoconference-equipped lecture rooms that facilitates the turning on of student microphones. It also has an indicator--a flashing blue ring--to let lecturers know that a student wishes to have their mic turned on. When the Take Next button is pressed, the blue ring becomes steady, the student's microphone goes live, and a camera frames that student and this image is visible to the lecturer on the confidence monitor and to the students on one of the large sceens. If more than one student presses their button, a queue forms, and each time the lecturer presses the Take Next button, the microphone of the next student in the queue is turned on.
Techsmith Relay
A screen recording program that is installed on the desktop of most University of Toronto lecture room computers. This product records the computer desktop display, such as a Powerpoint presentation, and the lecturer’s voice. Camtasia Relay recorders can be used by faculty, staff and students who have UTORID access to the lecture room computers. For further information: http://teaching.utoronto.ca/ed-tech/teaching-technology/lecture-capture
Telephone Calling at the Lectern (Teleconference)
In the videoconference-equipped lecture rooms, a telephone call can be connected so that everyone in the room can hear it, and the connected caller can hear anyone whose microphone is live. This requires set up by control room staff.
A device used primarily in the studio that allows a presenter to look into a camera and see text or their presentation at the same time.
TDHSC
See Terrence Donnelly Health Sciences Centre
Terrence Donnelly Health Sciences Centre
Two of the four videoconference-equipped lectures rooms are in this building located at University of Toronto Mississauga campus; the other two are in the Medical Sciences Building at the St. George campus in Toronto. Also known as the HSC, it was built in 2011 and houses the Mississauga Academy of Medicine.
The interface that is in the lecterns of the videoconference-equipped lecture rooms (and in many of the lecture rooms at U of T). In the videoconference-equipped lecture rooms, this panel provides access to lighting and sound control in the room, a map of the student microphones in the room, and the privacy button for the lecturer microphones, among other functions. Lecturers can become familiar with the touch panel to have more control over their presentations, or they can let control room staff provide support (the touch panel for each room is replicated in the control rooms).
Videoconference (appliance)
Technology that allows participants to see and hear each other via video in real time. Appliance videoconferencing is used when stable, good quality audio and video are required to effect natural communication across distance. The lecture rooms MSB3154, MSB3153, HSC130 & HSC140 use HD appliance videoconferencing to facilitate distance learning. Additionally, the Faculty of Medicine has several HD appliance-videoconference equipped rooms for meetings and seminars. Discovery Commons AV staff fully support videoconferences that use the appliance videoconference technology.
Videoconference (web) (aka webconference)
Technology that allows participants to see and hear each other via video in real time. Examples of web videconference tools are Zoom, Teams, and Skype.
Videoconference-Equipped Lecture Rooms
Two large lecture rooms in the Medical Sciences Building at St. George and two lecture rooms in the Terrence Donnelly Health Sciences Centre in Mississauga have cameras, student microphones, and appliance videoconference technology to facilitate distance learning between the two locations. Having two rooms equipped at each site means that two separate lectures can occur simultaneously, with lecturers presenting from either site. The rooms are: MSB3153, MSB3154, HSC130, HSC140.
Video Editing
The process of editing recorded video to remove unwanted video or to add video, titles, logos, sound effects, and music.
Video Production
Recording an event or scripted program using video camera(s), lighting and sound equipment. Videos can be recorded in a studio or in the field and can include a wide variety of variables depending on script requirements and budget.
A live media presentation that is also distributed synchronously online to many viewers over the internet via a streaming service. A one-to-many form of communication, participants can see and hear the event, but cannot be heard or seen; they often have the option of communicating to the event moderator and other participants via an integrated chat function. Discovery Commons has HD webcasting devices for live events. While webcasting, the event can also be recorded for later viewing on demand.
Wireless Microphone
Microphone that does not need a cable to transmit sound, and instead uses radio signals. Wireless microphones have the advantage that no cables get in the way of the presenter and avoid any trip hazards, but they require frequent battery refreshes for optimal sound.
Wireless Handheld Microphone
The MD Program has several wireless handheld microphones, available at both the downtown and Mississauga sites, that are used primarily at the front of the videoconference-equipped lecture rooms when panels of speakers are present.